Spatial filters in a GeoEvent Service filter GeoEvents based on a spatial relationship with a geofence. The geometries specifying a geofence must be imported into GeoEvent Server from a published feature service before a spatial filter can be configured.
The following spatial operators are supported:
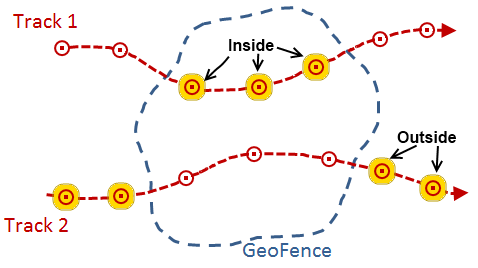
- INSIDE—A GeoEvent's geometry is considered to be inside a geofence if its geometry is entirely within the area defined by the geofence. This operator determines whether a point associated with a GeoEvent is inside an area of interest.
- OUTSIDE—A GeoEvent's geometry is considered to be outside a geofence if its geometry is entirely outside the area defined by the geofence. This operator determines whether a point associated with a GeoEvent is outside an area of interest.
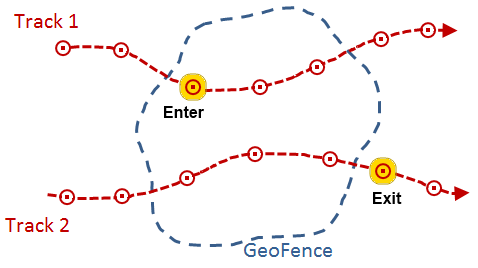
- ENTER—A GeoEvent's geometry is considered to have entered a geofence if its geometry is now inside the area defined by the geofence, when the previous GeoEvent position, from the same track, was outside the geofence. After an enter condition is detected and the GeoEvent is allowed to pass through the filter, the tracked object must report at least one event outside the geofence before another enter will be recognized.
- EXIT—A GeoEvent's geometry is considered to have exited a geofence if its geometry is now outside the area defined by the geofence, when the previous GeoEvent position, from the same track, was inside the geofence. After an exit condition is detected and the GeoEvent is allowed to pass through the filter, the tracked object must report at least one event inside the geofence before another exit will be recognized.
Typically, a set of geofences define areas of interest and are imported from a feature service providing polygon features. Geofences do not always have to represent polygonal areas; they can be imported from point and line features as well.
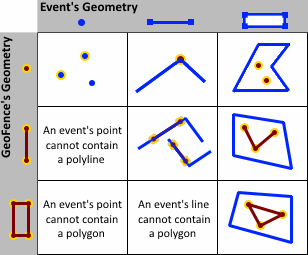
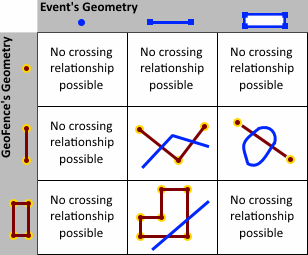
The spatial operators below can be used with different types of geometries. These spatial operators return a Boolean, indicating whether the described relationship exists between a geofence and a GeoEvent's geometry. Some relationships require that a GeoEvent's geometry have the same dimension as the geofence to which it is being compared, while others have more flexible dimensional constraints. Many of the spatial operators below are mutually exclusive Clementini operators.
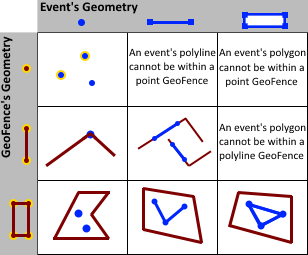
- CONTAINS—An event's geometry will contain a geofence if the geofence is a subset of the event's geometry and the intersection of the two geometries is not empty. Contains is the logical opposite of Within. It is not possible for a point geometry to contain a polyline or polygon, so it is not possible for a point associated with an event to contain a line or area imported as a geofence. It is possible for a point to contain a point or a line to contain a line, but testing for such a spatial relationship is not recommended. Trivial differences in a geometry due to projection may result in a point or line you expect to be coincident with a geofence not actually being perfectly coincident (in which case the Contains relationship will evaluate as false).
For more information on the Contains operator, see IRelationalOperator.Contains Method in the .NET API Reference.
- CROSSES—An event's geometry crosses a geofence if an
intersection exists in a geometry of a lesser dimension. Two
polylines cross if they intersect at one or more points and at
least one point is not an endpoint. A polyline and a polygon cross
if they share a polyline or a point on the interior of the polygon
which is not equivalent to the entire polyline. Crosses only applies to polyline/polyline,
polyline/polygon, or polygon/polyline relations. If either one of the geometries is empty, the
geometries do not cross.
For more information on the Crosses operator, see IRelationalOperator.Crosses Method in the .NET API Reference.
- DISJOINT—An event's geometry is considered to be
disjoint from a geofence if the two geometries do not intersect.
Note that an event's geometry can be disjoint from one geofence
while it intersects another geofence. Take care when specifying a
spatial expression. The expression will specify not only the
event's geometry, but also a scope, either any or all, and a set of
geofences identified using a regular expression pattern match
(for example,
SomeCategory/.*).
For more information on the Disjoint operator, see IRelationalOperator.Disjoint Method in the .NET API Reference.
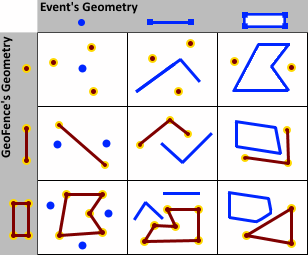
- EQUALS—An event's geometry equals a geofence's geometry if their symmetric difference is the empty set. If you were to iterate over each segment in each geometry and compare the segment's type and coordinates, and found they were the same (using the spatial reference's cluster tolerances to determine equality of coordinates), the two geometries would be considered equal.
For more information on the Equals operator, see IRelationalOperator.Equals Method in the .NET API Reference.
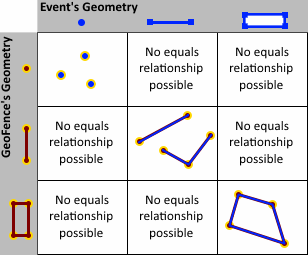
- INTERSECTS—An event's geometry intersects a geofence if the two geometries are not disjoint. Intersects is the logical opposite of Disjoint. An event's point that is within a geofence's area (polygon) also intersects the geofence. An event's polyline or polygon can intersect a geofence without being entirely within the geofence. An event's geometry can intersect one geofence within a set of geofences and still be DISJOINT ANY (for example, disjoint one or more). The event's geometry is not DISJOINT ALL since it intersects at least one of the geofences in the set.
- OVERLAPS—An event's geometry overlaps a geofence if an
intersection exists whose dimension is the same as the geometries
being considered and the intersection is not equivalent to either
the event's geometry or the geofence.
Overlaps only apply to polyline/polyline,
polygon/polygon, and multipoint/multipoint relations. If either one of the geometries is empty, the
geometries do not overlap.
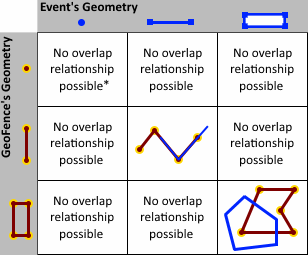
* Point geometries fail the equivalency condition, so an event's point location cannot overlap a geofence whose geometry is also a point.
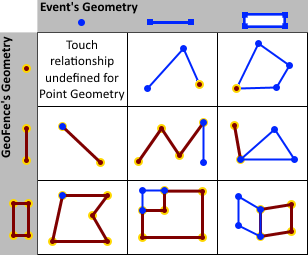
- TOUCHES—An event's geometry touches a geofence if an
intersection exists and the interior of the intersection is
empty. This means two geometries only touch at vertices
that define the geometry, not at a points in between
vertices. Touches is undefined for point/point
relations. If either one of the geometries is empty, the
geometries do not touch.
For more information on the Touches operator, see IRelationalOperator.Touches Method in the .NET API Reference.
- WITHIN—An event's geometry is considered to be within a geofence if the two geometries intersect and the intersection of their interiors is not empty. Within is the logical opposite of Contains.
For more information on the Within operator, see IRelationalOperator.Within Method in the .NET API Reference.
For more information on the relational operators, see IRelationalOperator Interface in the .NET API Reference.
For more information on working with geofences in GeoEvent Server, see Manage geofences.